Unlocking the Potential of SAP High Polymer Materials in the Medical Consumables Industry
Unlocking the Potential of SAP High Polymer Materials in the Medical Consumables Industry
In the ever-evolving landscape of materials science, SAP (Superabsorbent Polymer) has emerged as a remarkable innovation with diverse applications across various industries. In this article, we delve into the world of SAP high polymer materials, exploring their unique characteristics and highlighting their crucial role in the medical consumables sector.
**Understanding SAP High Polymer Materials:**
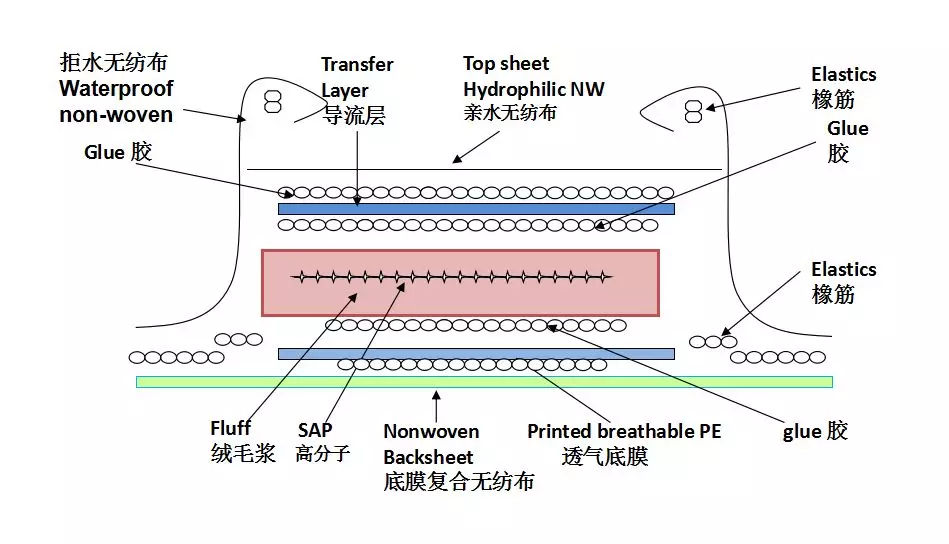
Superabsorbent polymers, or SAPs, are a class of materials renowned for their remarkable ability to absorb and retain large amounts of liquid relative to their own mass. This super-absorbency arises from the cross-linked structure of the polymer chains, which forms a three-dimensional network with a high density of hydrophilic groups. When these SAPs come into contact with water or bodily fluids, they swell and transform into a gel-like substance that traps the liquid, preventing leakage.
**Key Properties of SAP High Polymer Materials:**
1. **High Absorption Capacity:** SAPs can absorb several hundred times their weight in water or bodily fluids, making them incredibly efficient at retaining liquids.
2. **Retention and Locking:** They have the capacity to lock in absorbed fluids, preventing them from leaking back into the environment.
3. **Non-Toxicity:** SAPs are generally non-toxic, making them safe for various medical applications.
4. **Biocompatibility:** Many SAP formulations are biocompatible, allowing for safe contact with the human body.
**Applications in Medical Consumables:**
SAP high polymer materials find diverse applications in the field of medical consumables, enhancing both patient care and healthcare provider efficiency. Some key applications include:
1. **Wound Dressings:**
SAPs are integrated into wound dressings to create a moist healing environment. The absorbency of SAPs helps in wound exudate management, reducing the risk of infection and promoting faster healing. Additionally, SAPs minimize the need for frequent dressing changes, offering patient comfort and cost savings.
2. **Incontinence Products:**
Diapers, adult incontinence products, and feminine hygiene items benefit significantly from SAPs. Their high absorbency ensures effective containment of bodily fluids, maintaining dryness and comfort for users.
3. **Surgical Drapes and Gowns:**
SAPs are integrated into surgical drapes and gowns to manage and contain bodily fluids during surgeries. They play a vital role in maintaining a sterile surgical field, reducing the risk of cross-contamination.
4. **Ostomy Products:**
Ostomy pouches use SAPs to solidify and contain liquid waste, improving the quality of life for individuals with ostomies. This innovation promotes discretion, comfort, and ease of use.
5. **Hemostatic Agents:**
SAPs have found application as hemostatic agents to control bleeding during surgical procedures. They create a gel-like barrier to staunch blood flow, minimizing the need for traditional sutures or staples.
**Future Innovations and Sustainability:**
The use of SAP high polymer materials in medical consumables continues to evolve, with ongoing research focused on improving biocompatibility and sustainability. Researchers are exploring environmentally friendly SAP formulations, ensuring that these materials align with growing eco-consciousness in the medical field.
In conclusion, SAP high polymer materials represent a transformative innovation in the medical consumables industry. Their exceptional absorption and retention properties have revolutionized wound care, incontinence management, and various other medical applications. As research and development continue, we can expect to see even more innovative uses for SAPs, further enhancing patient care and advancing medical technologies.
 EN
EN
 AR
AR
 BG
BG
 HR
HR
 CS
CS
 DA
DA
 NL
NL
 FI
FI
 FR
FR
 DE
DE
 EL
EL
 HI
HI
 IT
IT
 JA
JA
 KO
KO
 NO
NO
 PL
PL
 PT
PT
 RO
RO
 RU
RU
 ES
ES
 SV
SV
 TL
TL
 IW
IW
 ID
ID
 LV
LV
 LT
LT
 SR
SR
 SK
SK
 VI
VI
 HU
HU
 TH
TH
 TR
TR
 FA
FA
 GA
GA
 CY
CY
 IS
IS
 LA
LA