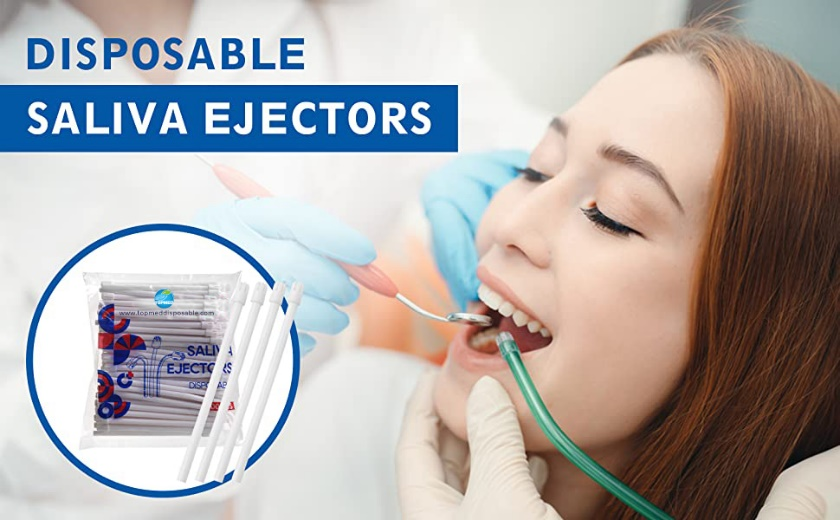
The Dental Saliva Ejector: An Essential Tool in Dentistry
Here is the content:
- Origin and Historical Development
- Material Characteristics and Key Features
- Applications and Related Dental Consumables
Origin and Historical Development
The Dental Saliva Ejector, also known as a dental suction, is a vital tool used in dentistry to remove saliva, water, and debris from the patient's mouth during various dental procedures. Its invention and subsequent development have significantly improved patient comfort and oral hygiene during dental treatments.
The origin of the Dental Saliva Ejector can be traced back to the early 20th century. In 1880, Dr. C. Edmund Kells introduced the first oral evacuator, which consisted of a rubber bulb attached to a metal tube. This rudimentary device allowed dentists to manually suction fluids from the oral cavity. However, it was not until the 1920s that more advanced versions of the Saliva Ejector began to emerge.
Dr. William T. Green Morton, a dentist from New York, is credited with inventing the modern Dental Saliva Ejector in 1928. His design incorporated a metal suction tip connected to a low-powered vacuum system. This innovation marked a significant milestone in dentistry, as it enabled a more efficient and controlled method of evacuating saliva and debris from the patient's mouth.
Over the years, the Dental Saliva Ejector underwent further improvements in terms of design, materials, and functionality. The introduction of plastic materials in the 1950s revolutionized the manufacturing process, making the ejectors more affordable and disposable. These advancements led to widespread adoption and integration of the Dental Saliva Ejector as a standard instrument in dental clinics and hospitals worldwide.
Material Characteristics and Key Features
Modern Dental Saliva Ejectors are typically made from high-quality plastic materials such as polypropylene or polyethylene. These materials offer several key characteristics that make them suitable for dental applications. Firstly, they are non-toxic and hypoallergenic, ensuring the safety and comfort of patients during use. Additionally, plastic ejectors are lightweight, flexible, and resistant to moisture and corrosion.
The design of the Dental Saliva Ejector incorporates several important features. The main component is the suction tip, which is tapered and smooth to prevent injury to soft tissues in the mouth. The tip is connected to a long, thin, and flexible hose that allows for easy maneuverability and access to all areas of the oral cavity. The other end of the hose is connected to a vacuum system, which generates the necessary suction power to remove fluids and debris effectively.
Applications and Related Dental Consumables
The Dental Saliva Ejector finds extensive application in various dental procedures and clinical settings. It is used during routine check-ups, dental cleanings, restorative treatments, and surgical procedures. By removing saliva and excess water from the oral cavity, it provides a clear field of vision for the dentist, allowing for accurate diagnosis and treatment.
In addition to the Dental Saliva Ejector, several related dental consumables are used in conjunction with this instrument to optimize its functionality. Dental aspirator tips, also made of plastic, are attached to the suction tip to enhance fluid evacuation. Disposable saliva ejector traps are used to collect debris and prevent clogging of the vacuum system. These consumables ensure hygienic and efficient operation of the Dental Saliva Ejector.
In conclusion, the Dental Saliva Ejector has a rich history of development and has become an indispensable tool in modern dentistry. Its evolution from simple rubber bulbs to advanced plastic designs has revolutionized dental procedures, improving patient comfort and clinical outcomes. With its material characteristics, key features, and diverse applications, the Dental Saliva Ejector continues to play a crucial role in maintaining oral health and enhancing the overall dental experience for patients worldwide.

 EN
EN
 AR
AR
 BG
BG
 HR
HR
 CS
CS
 DA
DA
 NL
NL
 FI
FI
 FR
FR
 DE
DE
 EL
EL
 HI
HI
 IT
IT
 JA
JA
 KO
KO
 NO
NO
 PL
PL
 PT
PT
 RO
RO
 RU
RU
 ES
ES
 SV
SV
 TL
TL
 IW
IW
 ID
ID
 LV
LV
 LT
LT
 SR
SR
 SK
SK
 VI
VI
 HU
HU
 TH
TH
 TR
TR
 FA
FA
 GA
GA
 CY
CY
 IS
IS
 LA
LA